728x90
반응형
목적
- 탐색 알고리즘에서 사용되는 표현 방식을 이해하고 직접 구현
- 탐색 알고리즘인 DFS(Depth First Search, 깊이 우선 탐색) 알고리즘에 대해 이해하고 직접 구현
- 탐색 알고리즘인 BFS(Breadth First Search, 너비 우선 탐색) 알고리즘에 대해 이해하고 직접 구현
인접리스트와 인접 행렬

위 와 같은 그래프가 있을 때, 이 그래프를 표현하는 방식은 크게 2가지(인접리스트, 인접행렬)가 있다.
각 표현 방식을 구현해보면 다음 코드와 같다.
1) 간선을 인접리스트로 변환
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
// 만들어진 그래프를 출력
void print_adjacency_list(map<int, vector<int>> graph) {
for (auto node : graph) {
cout << node.first << " : ";
for (auto ns : node.second) {
cout << ns << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
int main() {
int n, m, u, v;
// 최초 입력 받기
cin >> n >> m >> start_node;
// 그래프를 인접리스트 형식으로 표현
map<int, vector<int>> graph;
// 간선의 개수만큼 노드에 추가
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
// 각 노드별로 연결된 간선을 서로 추가(무방향 또는 양방향 그래프)
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// 생성된 인접리스트 출력
print_adjacency_list(graph);
return 0;
}
2) 간선을 인접행렬로 변환
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, m, u, v;
cin >> n >> m;
// 인접행렬 생성
int** graph = new int* [n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new int[n];
}
// 인접행렬 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
graph[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 간선 입력
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
u--;
v--;
// 무방향 그래프
graph[u][v] = graph[v][u] = 1;
}
// 인접행렬 출력
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cout << graph[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
3) 인접행렬을 문자열로 입력받기
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
string str;
cin >> n;
int** map = new int* [n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
str = "";
map[i] = new int[n];
cin >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) {
map[i][j] = str[j] - '0';
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j< n; j++) {
cout << map[i][j];
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
4) 인접행렬을 인접리스트로 변환
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> *Convert_adjMatrix_to_adjList(int n, int** matrix) {
vector<int> * adjlist = new vector<int>[n+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == 1 && i != j) {
adjlist[i+1].push_back(j+1);
}
}
sort(adjlist[i+1].begin(), adjlist[i+1].end());
}
return adjlist;
}
int main() {
int n;
string str;
cin >> n;
int** map = new int* [n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
str = "";
map[i] = new int[n];
cin >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < str.length(); j++) {
map[i][j] = str[j] - '0';
}
}
vector<int> *adl = Convert_adjMatrix_to_adjList(n, map);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << i << " : ";
for (auto node : adl[i]) {
cout << node << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
DFS (깊이 우선 탐색)
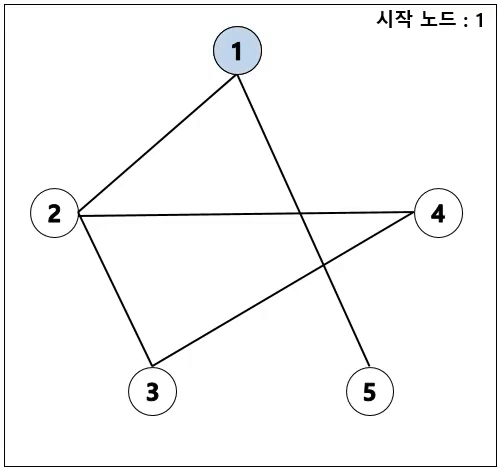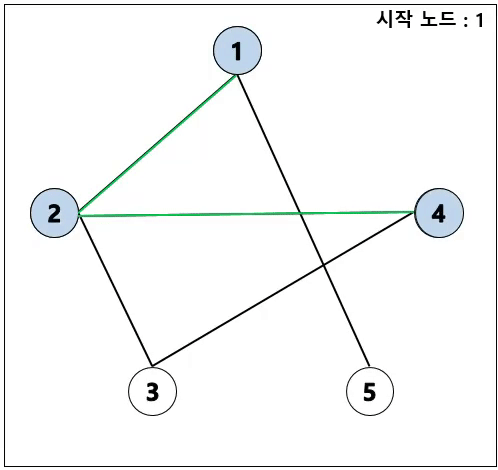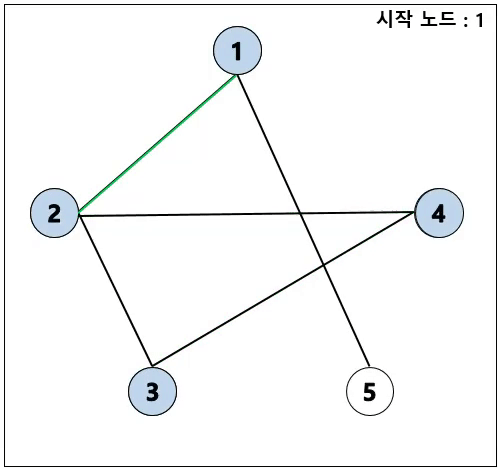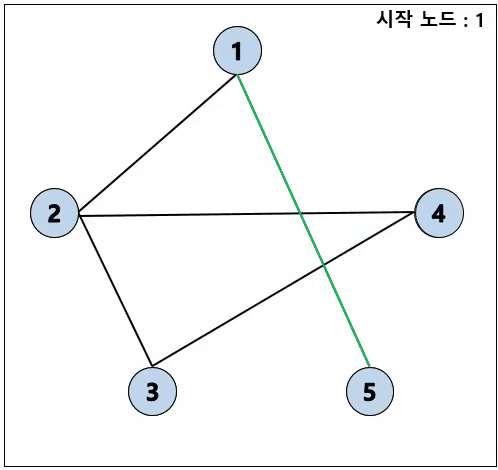
- 재귀로 DFS 구현
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
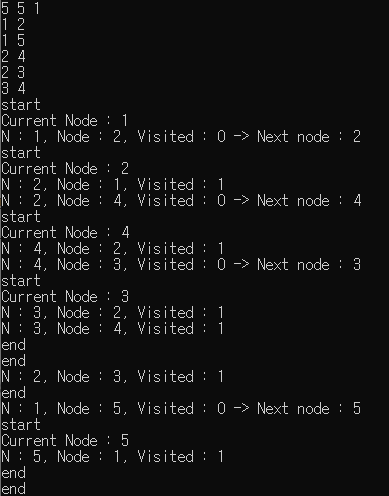
void dfs_recursion(int n, vector<int>* graph, bool* visited) {
cout << "start\nCurrent Node : " << n << "";
// 시작노드의 방문 여부를 체크
visited[n] = true;
for (auto node : graph[n]) {
cout << "\nN : " << n << ", Node : " << node << ", Visited : " << visited[node] << " ";
// 노드가 방문이 되어있는지 확인
if (!visited[node]) {
cout << "-> Next node : " << node << "\n";
// 방문 안된 노드의 키값을 넣음
func_1260_dfs_recursion(node, graph, visited);
}
}
cout << "\nend";
}
int main() {
int n, m, start_node, u, v;
cin >> n >> m >> start_node;
vector<int> *graph = new vector<int>[n+1];
bool *visited = new bool[n+1];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(bool) * (n+1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
/*
// 오름차순으로 각 벡터를 정렬시킴 (이부분 주석 해제 시 1 2 3 4 5 순서로 진행)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
*/
dfs_recursion(start_node, graph, visited);
return 0;
}
- 스택으로 DFS 구현
//
BFS (너비 우선 탐색)

- 큐로 BFS 구현
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#incldue<queue>
using namespace std;
void bfs_queue(int n, vector<int> * graph, bool* visited) {
queue<int> q;
int now_node;
visited[n] = true;
q.push(n);
while (!q.empty()) {
now_node = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << now_node << " ";
for (auto node : graph[now_node]) {
if (!visited[node]) {
visited[node] = true;
q.push(node);
}
}
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
int n, m, start_node, u, v;
cin >> n >> m >> start_node;
vector<int> *graph = new vector<int>[n+1];
bool *visited = new bool[n+1];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(bool) * (n+1));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sort(graph[i].begin(), graph[i].end());
}
bfs_queue(start_node, graph, visited);
return 0;
}
728x90
반응형
'코딩테스트 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 다익스트라(Dijkstra) (0) | 2022.04.11 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 우선순위 큐 - 작성 중 (0) | 2022.04.11 |
| [알고리즘] 하노이의 탑 (0) | 2022.03.09 |
| [알고리즘] 달팽이 배열 채우기 (0) | 2021.11.06 |
| [알고리즘] 함수 (0) | 2021.10.11 |
| [알고리즘] 0 ~ N 사이의 소수 개수 구하기 (2) | 2020.05.19 |