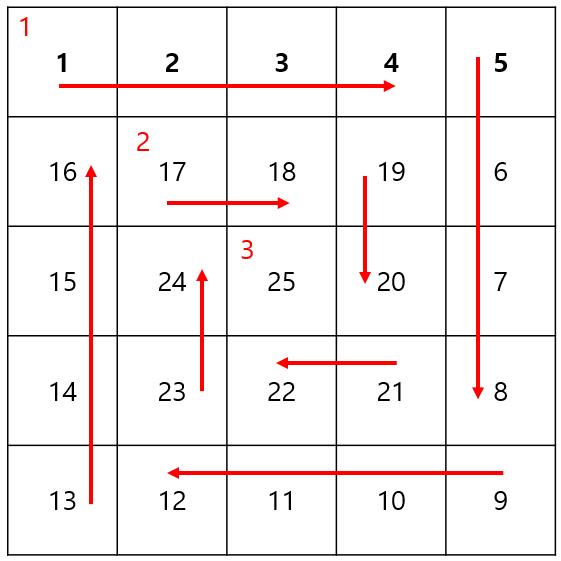
문제 1. 최소, 최대
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int min(vector<int>& arr) {
int min = arr.front();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr.at(i) < min) {
min = arr.at(i);
}
}
return min;
}
int max(vector<int>& arr) {
int max = arr.front();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr.at(i) > max) {
max = arr.at(i);
}
}
return max;
}
int main() {
int a, tmp;
vector<int> arr;
cin >> a;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++){
cin >> tmp;
arr.push_back(tmp);
}
cout << min(arr) << " " << max(arr);
return 0;
}
문제 2. 최댓값
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int tmp, max;
vector<int> arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
cin >> tmp;
arr.push_back(tmp);
}
max = arr.front();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
if (arr.at(i) >= max) {
max = arr.at(i);
tmp = i+1;
}
}
cout << max << endl;
cout << tmp;
return 0;
}
문제 3. 숫자의 개수
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b, c;
int arr[10] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
string str_abc;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
str_abc = to_string(a * b * c);
for (int i = 0; i < str_abc.length(); i++) {
arr[int(char(str_abc[i])) - int('0')]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
문제 4. 나머지
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> arr;
int a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cin >> a;
arr.push_back(a % 42);
}
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
arr.erase(unique(arr.begin(), arr.end()), arr.end());
cout << arr.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
문제 5. 평균
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, max;
double aver=0;
cin >> a;
int* arr = new int[a];
double* arr2 = new double[a];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
cin >> arr[i];
if (i == 0) {
max = arr[0];
}
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
arr2[i] = double(arr[i]) / max * 100;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
aver += arr2[i];
}
cout.precision(6);
cout << aver / a << endl;
return 0;
}
문제 6. OX퀴즈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int point(string str) {
bool is_flag = false;
int cnt = 1, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= str.size(); i++) {
if (str[i] == 'O') {
if(is_flag) cnt++;
is_flag = true;
sum += cnt;
}
else {
cnt = 1;
is_flag = false;
}
}
return sum;
}
int main() {
int a;
cin >> a;
int* arr = new int[a];
string* str_arr = new string[a];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
cin >> str_arr[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
cout << point(str_arr[i]) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
문제 7. 평균은 넘겠지
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a, b, sum, cnt, all;
double aver;
cin >> a;
vector<int *> vec;
char str_tmp[100];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
cin >> b;
int* arr = new int[b + 1];
arr[0] = b;
for (int j = 1; j <= b; j++) {
cin >> arr[j];
}
vec.push_back(arr);
}
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
all = int(vec.at(i)[0]);
sum = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= all; j++) {
sum += vec.at(i)[j];
}
aver = double(sum) / all;
cnt = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= all; j++) {
if (aver < vec.at(i)[j]) {
cnt += 1;
}
}
sprintf(str_tmp, "%.3f", double(cnt) / all * 100);
cout << str_tmp << "%" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
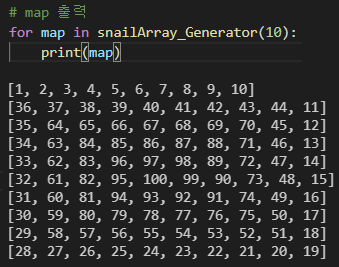
결과

'코딩테스트 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > 기본 수학 1 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.18 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > 문자열 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.15 |
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > 함수 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.14 |
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > while문 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.14 |
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > for문 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.13 |
| [백준] 단계별로 풀어보기 > if문 (c++) (0) | 2022.01.12 |